Vulnerability Review – August 2025
This blog is a recap of the most critical vulnerabilities disclosed between 01 August and 31 August 2025 that most likely impact software utilized by managed service providers (MSPs). While not all MSPs use the software discussed in this blog, the software has been labeled as a priority software by Blackpoint’s APG due to the overall number of MSPs/organizations that use it.
Key Findings
- There were more than 3,500 vulnerabilities disclosed between 01 August and 31 August 2025, with more than 1,800 vulnerabilities being scored with a high or critical Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) rating.
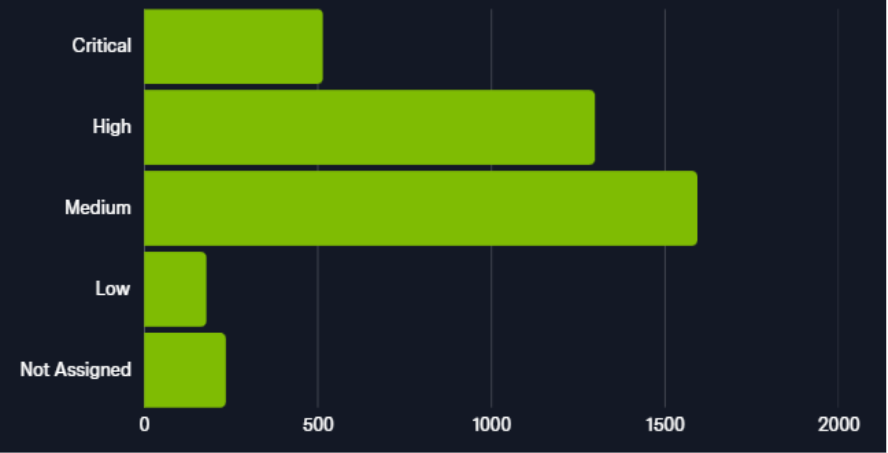
- There are several that have been actively exploited and 15 that have been added to the U.S. CISA Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) Catalog, indicating reliable reports of active exploitation.
- Blackpoint’s APG assesses with high confidence that threat actors will continue to leverage known and unknown vulnerabilities in ubiquitous software and services over the next 12 months.
Vulnerabilities
Network Edge Devices
Network edge devices – firewalls, routers, VPN gateways, etc. – are the critical gatekeepers between internal networks and the internet. These devices manage and filter traffic, enforce security policies, and often provide remote access capabilities making them high-value targets for threat actors. Edge devices often operate with elevated privileges and are typically exposed to the internet, they’re frequently targeted via vulnerabilities, exposed devices, or misconfigurations.
Cisco Firewall Management Center (FMC)
Cisco released patches for a critical vulnerability impacting Secure Firewall Management Center (FMC) software. Cisco FMC is a unified, centralized platform for managing and monitoring Cisco’s security solutions and provides comprehensive management of firewall policies, intrusion prevention, malware defense, application control, and URL filtering across deployments.
The vulnerability, CVE-2025-20265 (CVSS 10) is a remote unauthenticated command injection vulnerability in the RASIUS authentication feature of Cisco FMC. For the vulnerability to be exploited, Cisco Secure FMC Software must be configured for RADIUS authentication for the web-based management interface, SSH management, or both. This vulnerability impacts Cisco Secure FMC Software releases 7.0.7 and 7.7.0.
A threat actor could exploit this vulnerability by sending crafted input during the authentication process, potentially gaining the ability to execute commands at a high privileged level. With this level of access, the threat actor could disable protection, insert malicious rules, deploy persistence mechanisms, and move laterally throughout the network.
SonicWall Firewalls
This month, Blackpoint’s SOC and external researchers began reporting a significant increase in threat actors targeting of SonicWall firewall devices where SSL VPN is enabled. At the time of observation and initial reporting, there were multiple reports of a potential zero-day vulnerability impacting the devices. However, after an investigation, SonicWall reported that no zero-day vulnerability had been identified and instead threat actors, including Akira Ransomware operators, were very likely exploiting CVE-2024-40766, which was disclosed and patched in August 2024.
CVE-2024-40766 (CVSS 9.8) is an improper access control vulnerability that was quickly targeted by multiple threat groups, including Fog and Akira Ransomware operations, to gain initial access via SSL VPN and gain access to sensitive environments and deploy malware payloads.
While this targeting was likely not the result of a new vulnerability, it has been included due to the criticality of these devices and the level of recent targeting by multiple threat actors. Threat actors, especially financially motivated groups, often show renewed interest in older vulnerabilities when vulnerable devices are identified. These threat actors are often opportunistic and when vulnerable devices are identified, it is likely these groups will target it due to the level of access they can gain and the impact they can have with a successful attack.
Backup and Disaster Recovery (BDR) Solutions
Backup and Disaster Recovery (BDR) solutions are considered critical business software for MSPs as they ensure business continuity, support regulatory compliance, and serve as a last line of defense during incidents, such as ransomware attacks. BDR platforms often centralize data across multiple clients, making them an attractive target for threat actors. A successful attack on a BDR solution could allow threat actors to delete or encrypt backups, exfiltrate sensitive client data, move laterally through the network, or launch devastating supply chain attacks.
Commvault
Commvault released patches for two vulnerabilities, CVE-2025-57791 and CVE-2025-57790, impacting Commvault. Affected versions include 11.32.0–11.32.101 (fixed in 11.32.102), 11.36.0–11.36.59 (fixed in 11.36.60), and 11.38.20–11.38.25 (fixed in 11.38.32). Commvault SaaS is not affected.
- CVE-2025-57791 (CVSS 6.9) is an argument injection vulnerability that can be abused to bypass authentication.
- CVE-2025-57790 (CVSS 8.7) is a path traversal vulnerability that could allow threat actors to drop a JSP web shell into webroot.
These two vulnerabilities could be chained together to allow remote code execution on the server; then a threat actor could disable or corrupt backups, exfiltrate sensitive data, and deploy malware including backdoors, remote access trojans, and ransomware.
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Identity and access management (IAM) products are systems that control who can access what within an organization’s digital environment. These products handle authentication and authorization, managing everything from user accounts and passwords to single sign-on (SSO), multi-factor authentication (MFA), and privileged access. Threat actors can exploit these devices to impersonate users, elevate privileges, bypass security controls, and move laterally across networks. Threat actors can target these devices to takeover accounts, exfiltrate data, gain persistence, and deploy malware.
Securden Unified PAM
Securden released patches for multiple vulnerabilities impacting Unified PAM, the vulnerabilities were patched in version 11.4.4.
- CVE-2025-53118 (CVSS 9.8) is an authentication bypass vulnerability that allows an unauthenticated attacker to control administrator backup functions, which could lead to compromise of passwords, secrets, and application session tokens.
- CVE-2025-53119 (CVSS 7.5) is an unauthenticated unrestricted file upload vulnerability that allows an attacker to upload malicious binaries and scripts to the server.
- CVE-2025-53120 (CVSS 9.4) is a path traversal vulnerability in unauthenticated upload functionality that allows a malicious actor to upload binaries and scripts to the server’s configuration and web root directories, achieving remote code execution.
A proof-of-concept (PoC) does exist for these vulnerabilities and there is an even chance the PoC could allow lower-skill level threat actors to exploit them. Successful exploitation of these vulnerabilities could result in domain-wide compromise indicating these are likely to be an attractive target for threat groups.
Remote Management and Monitoring (RMM)
RMM tools are considered priority software by Blackpoint’s APG as they are designed to allow remote access to a company’s IT infrastructure. They are frequently used by IT teams to remotely manage the infrastructure including troubleshooting problems, applying patches, colling data that can be used to generate reports, and automating routine tasks.
These factors make them an attractive target and tool for threat actors and could provide persistent access to compromised environments. By using legitimate tools threat actors are not required to maintain the resources or skills to develop and maintain their own variants, have a better chance of blending in with legitimate network activity, and can enable file sharing which allows threat actors to easily execute additional tools or malware.
N-able N-central
N-able released patches for two vulnerabilities impacting N-central, a remote monitoring and management (RMM) platform designed for managed service providers (MSPs). These vulnerabilities require authentication to exploit; however, threat actors have historically been reported to successfully gain unauthorized access to tools, like N-central, for initial access and persistence.
- CVE-2025-8875 is an insecure deserialization vulnerability that could lead to command execution
- CVE-2028-8876 is a command injection vulnerability via improper sanitization of user input
These vulnerabilities were added to CISA’s KEV Catalog on August 13, 2025, indicating reliable reports of active exploitation. Additional details related to the exploitation have not been released, likely in an attempt to provide organizations with time to patch.
Blackpoint’s APG Analysis
Blackpoint’s SOC consistently monitors and actions lateral movement and remote execution within our customer’s environments. Additionally, Blackpoint has detections in place to identify the behaviors associated with the vulnerabilities detailed within this blog.
Blackpoint’s APG assesses with high confidence that threat actors will continue to target, or begin targeting, these vulnerabilities over the next 12 months to deploy malware, steal sensitive information, and gain unauthorized access to organizations. It is likely that these vulnerabilities will be targeted by multiple types of threat actors, including both nation-state and financially motivated threat actors over the next 12 months.
References