Vulnerability Review – July 2025
This blog is a recap of the most critical vulnerabilities disclosed between 01 July and 31 July 2025 that most likely impact software utilized by managed service providers (MSPs). While not all MSPs use the software discussed in this blog, the software has been labeled as a priority software by Blackpoint’s APG due to the overall number of MSPs/organizations that use it.
Key Findings
There were more than 3,800 vulnerabilities disclosed between 01 July and 31 July 2025, with more than 1,700 vulnerabilities being scored with a high or critical Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) rating.
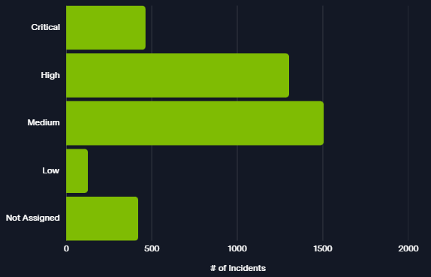
There are several that have been actively exploited and 20 that have been added to the U.S. CISA Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) Catalog, indicating reliable reports of active exploitation.
Blackpoint’s APG assesses with high confidence that threat actors will continue to leverage known and unknown vulnerabilities in ubiquitous software and services over the next 12 months.
Vulnerabilities
Critical Enterprise Software
Critical Enterprise Software includes products and software that are essential to business continuity and operations. These tools support internal and external communication, host web and application services, and facilitate storage, management and sharing for files and data. Threat actors often target such systems to steal sensitive information establish initial access, deploy backdoors and web shells, harvest user credentials and privileged information, and map out additional areas of the network for further exploitation.
VMware ESXi, Workstation, and Fusion
Updates were released to address multiple critical vulnerabilities impacting VMware ESXi, Workstation, and Fusion. While there was no evidence of publicly available proof-of-concept (PoC) or active exploitation, VMware products are an attractive target for threat actors due to the type of data these products have and the ability to hop from these products to the wider network.
- CVE-2025-41236 (CVSS 9.3) is an integer overflow vulnerability that exists in the VMXNET3 virtual network adapter that could allow a threat actor wil local administrative privileges to execute code on the host system.
- CVE-2025-41237 (CVSS 9.3) is an integer-overflow vulnerability that impacts the Virtual Machine Communication Interface (VMCI) that could allow a local administrative user on a virtual machine to execute code as the VMX process on the host system.
- CVE-2025-41237 (CVSS 9.3) is an integer-overflow vulnerability that impacts the Virtual Machine Communication Interface (VMCI) that could allow a local administrative user on a virtual machine to execute code as the VMX process on the host system.
- CVE-2025-41238 (CVSS 9.3) is a heap overflow vulnerability impacting the paravirtualized SCSI controller that could allow a local administrative user on a virtual machine to execute code as the VMX process on the host system.
- CVE-2025-41239 (CVSS 7.1) is an information disclosure vulnerability that could allow a user with local administrative privileges to leak memory from processes communicating with vSockets.
Blackpoint’s APG has tracked multiple threat actors that have historically targeted vulnerabilities impacting VMware ESXi, Workstation, and Fusion including Black Basta and Akira Ransomware operations and threat actors tracked as Octo Tempest and Manatee Tempest.
Wing FTP
Researchers disclosed a critical vulnerability impacting Wing FTP server prior to version 7.4.4. This vulnerability reportedly has several PoCs available and has been actively exploited since at least July 01, 2025. The vulnerability has reportedly been exploited to download and execute malicious files, perform reconnaissance, and install remote monitoring and management (RMM) software.
CVE-2025-47812 (CVSS 10) is a remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability that allows injection of arbitrary Lua code into user session files that ultimately could lead to RCE. This vulnerability was added to CISA’s KEV Catalog on July 14, 2025.
In order to exploit, threat actors must authenticate via credentials or an anonymous FTP account. The anonymous account does not require a password but is reportedly disabled by default.
Many organizations rely on FTP servers to host sensitive data and ensure continuity of operations. These servers are often targeted by threat actors because they are frequently exposed to the internet, misconfigured, or running outdated versions; these factors make them ideal for credential theft, data exfiltration, malware deliver, and initial access points.
Network Edge Devices
Network edge devices – firewalls, routers, VPN gateways, etc. – are the critical gatekeepers between internal networks and the internet. These devices manage and filter traffic, enforce security policies, and often provide remote access capabilities making them high-value targets for threat actors. Edge devices often operate with elevated privileges and are typically exposed to the internet, they’re frequently targeted via vulnerabilities, exposed devices, or misconfigurations.
Fortinet FortiWeb
Fortinet released patches for a critical vulnerability impacting FortiWeb versions 7.6.0-7.6.3, 7.4.0-7.4.7, 7.2.0-7.2.10, and below 7.0.10. The root cause of the vulnerability is reportedly a function called get_fabric_user_by_token, which is part of the Fabric Connector component that serves as a bridge between FortiWeb and other Fortinet products.
CVE-2025-25257 (CVSS 9.6) is an unauthenticated SQL injection vulnerability that stems from the improper neutralization of special elements used in SQL statements. This vulnerability could allow an unauthenticated attacker to execution unauthorized SQL commands through crafted HTTP or HTTPS requests. Additionally, the attack could escalate to remote code execution by using a SELECT… INTO OUTFILE statement to write a malicious payload to the file system. The attacker could drop a file onto the underlying operating system and potentially execute it via Python.
This vulnerability has been actively exploited and reportedly targeted to deploy web shell malware onto at least 80 FortiWeb instances, with the majority of the instances in the United States. This vulnerability was added to CISA’s KEV Catalog on July 18, 2025.
GFI KerioControl
Patches were released for multiple vulnerabilities impacting GFI KerioControl. These vulnerabilities have publicly available PoCs indicating that they could be exploited by lower-level threat actors that do not possess the knowledge and sophistication to exploit them.
- CVE-2025-34071 (CVSS 9.4) is a RCE vulnerability impacting GFI Kerio Control 9.4.5. The system upgrade mechanism accepts unsigned .img files, which can be modified to include malicious scripts within the upgrade.sh or disk image components. These modified upgrade images are not validated for authenticity or integrity, and are executed by the system post-upload, enabling root access.
- CVE-2025-34070 (CVSS 10) is a missing authentication vulnerability impacting the GFIAgent component of GFI Kerio Control 9.4.5. The GFIAgent service, responsible for integration with GFI AppManager, exposes HTTP services on ports 7995 and 7996 without proper authentication. The /proxy handler on port 7996 allows arbitrary forwarding to administrative endpoints when provided with an Appliance UUID, which itself can be retrieved from port 7995. This results in a complete authentication bypass, permitting access to sensitive administrative APIs.
- CVE-2025-34069 (CVSS 9.6) is an authentication bypass vulnerability impacting GFI Kerio Control 9.4.5; it is due to insecure default proxy configuration and weak access control in the GFIAgent service. Successful exploitation enables unauthenticated attackers to access the GFIAgent service on ports 7995 and 7996, retrieve the appliance UUID, and issue administrative requests via the proxy. Exploitation results in full administrative access to the Kerio Control appliance.
Threat actors are likely to find this an attractive target because KerioControl sits between an organization’s internal network and the internet and could allow threat actors to bypass security controls, establish persistence, move laterally into the network, and leverage the VPN functionality to impersonate users.
Collaboration and Communication Tools
Collaboration and communication tools are essential for MSPs to manage their internal operations, coordinate with clients, and streamline service delivery. These types of tools often store sensitive conversations, documentation, credentials, and product data. A successful attack targeting collaboration and communication tool could allow a threat actor to intercept communications, harvest sensitive data, hijack projects, or impersonate MSP staff to conduct phishing attacks.
Microsoft SharePoint
Microsoft released security updates for SharePoint Subscription Edition and SharePoint 2019 – both vulnerabilities impact on-premises SharePoint Servers only. Microsoft SharePoint is often deeply integrated into Microsoft’s platform, including Teams, OneDrive, and Outlook, which all maintain valuable information.
- CVE-2025-53770 (CVSS 9.8) is a remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability. This vulnerability was added to CISA’s KEV Catalog on July 20, 2025.
- CVE-2025-53771 (CVSS 9.8) is a spoofing vulnerability.
These vulnerabilities are related to two other SharePoint vulnerabilities, CVE-2025-49704 and CVE-2025-49706, which could be chained together to achieve remote code execution. The exploit chain, dubbed “ToolShell”, was patched in Microsoft’s July 2025 Patch Tuesday.
These vulnerabilities have been actively exploited to target dozens of organizations including those in the financials, academics, and government verticals, beginning around July 18, 2025. The threat actors reportedly exploited the vulnerabilities to gain access to the SharePoint Server, exfiltrated sensitive data, deployed persistent backdoors, and stolen cryptographic keys.
Workflow Automation Tools
Workflow automation tools are critical for streamlining business processes by connecting appliances, orchestrating tasks, and automating data flows across systems. These tools are often deeply integrated and maintain elevated permissions within an organization’s environment indicating they are attractive targets for threat actors. Threat actors target these platforms to hijack automated workflows, deploy malware at scale, exfiltrate sensitive data, and move laterally through these connected systems. Compromising these tools provides attackers with a powerful foothold to disrupt operations or abuse trusted automation channels.
Schneider Electric Ecostruxure
Schneider Electric issued a critical security advisory warning of six vulnerabilities impacting its EcoStruxure IT Data Center Expert (DCE) software. These vulnerabilities impact versions 8.3 and prior and Schneider Electric has released version 9.0 to address these.
- CVE-2025-50121 (CVSS 10) an OS Command Injection vulnerability that could allow unauthenticated remote code execution though the web interface when HTTP is enabled; however, this is disabled by default.
- CVE-2025-50122 (CVSS 8.3) an Insufficient Entropy vulnerability that could allow a threat actor to discover the root password through reverse engineering of installation or upgrade artifacts.
- CVE-2025-50123 (CVSS 7.2) an improper control of generation of code vulnerability that could cause remote command execution by a privileged account when the server is accessed via a console and through exploitation of the hostname input.
- CVE-2025-50124 (CVSS 5.9) an improper privilege management vulnerability that could allow a threat actor to elevate privileges when the server is accessed by a privileged account via a console and through exploitation of a setup script.
- CVE-2025-50125 (CVSS 6.4) SSRF vulnerability that could allow unauthenticated remote code execution when the server is accessed via the network with knowledge of hidden URLs and manipulation of host request header.
- CVE-2025-6438 (CVSS 6.1) a XXE vulnerability that could allow a threat actor to manipulate SOAP API calls and SML external entities injection resulting in unauthorized file access when the server is access via the network using an application account.
While there are no publicly available reports of these vulnerabilities being actively exploited; this software provides centralized monitoring and management capabilities. Threat actors could gain access and potentially control the operational layer of the data center. Additionally, due to the type of industry verticals Schneider Electric serves, the organizations are likely an attractive target for both financially motivated and nation-state threat groups.
Blackpoint’s APG Analysis
Blackpoint’s SOC consistently monitors and actions lateral movement and remote execution within our customer’s environments. Additionally, Blackpoint has detections in place to identify the behaviors associated with the vulnerabilities detailed within this blog.
Blackpoint’s APG assesses with high confidence that threat actors will continue to target, or begin targeting, these vulnerabilities over the next 12 months to deploy malware, steal sensitive information, and gain unauthorized access to organizations. It is likely that these vulnerabilities will be targeted by multiple types of threat actors, including both nation-state and financially motivated threat actors over the next 12 months.